Strengthening Nigeria’s COVID-19 Response
Challenge
The COVID-19 pandemic presented a daunting communications challenge for public health authorities. The country announced the lockdowns as misinformation and conspiracies surrounding the COVID-19 virus gained ground in the country, with the potential to undermine public compliance with public health and social measures. To combat this threat, the Nigerian Center for Disease Control (NCDC) sought Gatefield as a strategic ally.
Gatefield partnered with the NCDC on its #TakeResponsibility campaign and launched a strategic national emergency and risk communications campaign to empower citizens and residents with accurate information during a time of uncertainty.

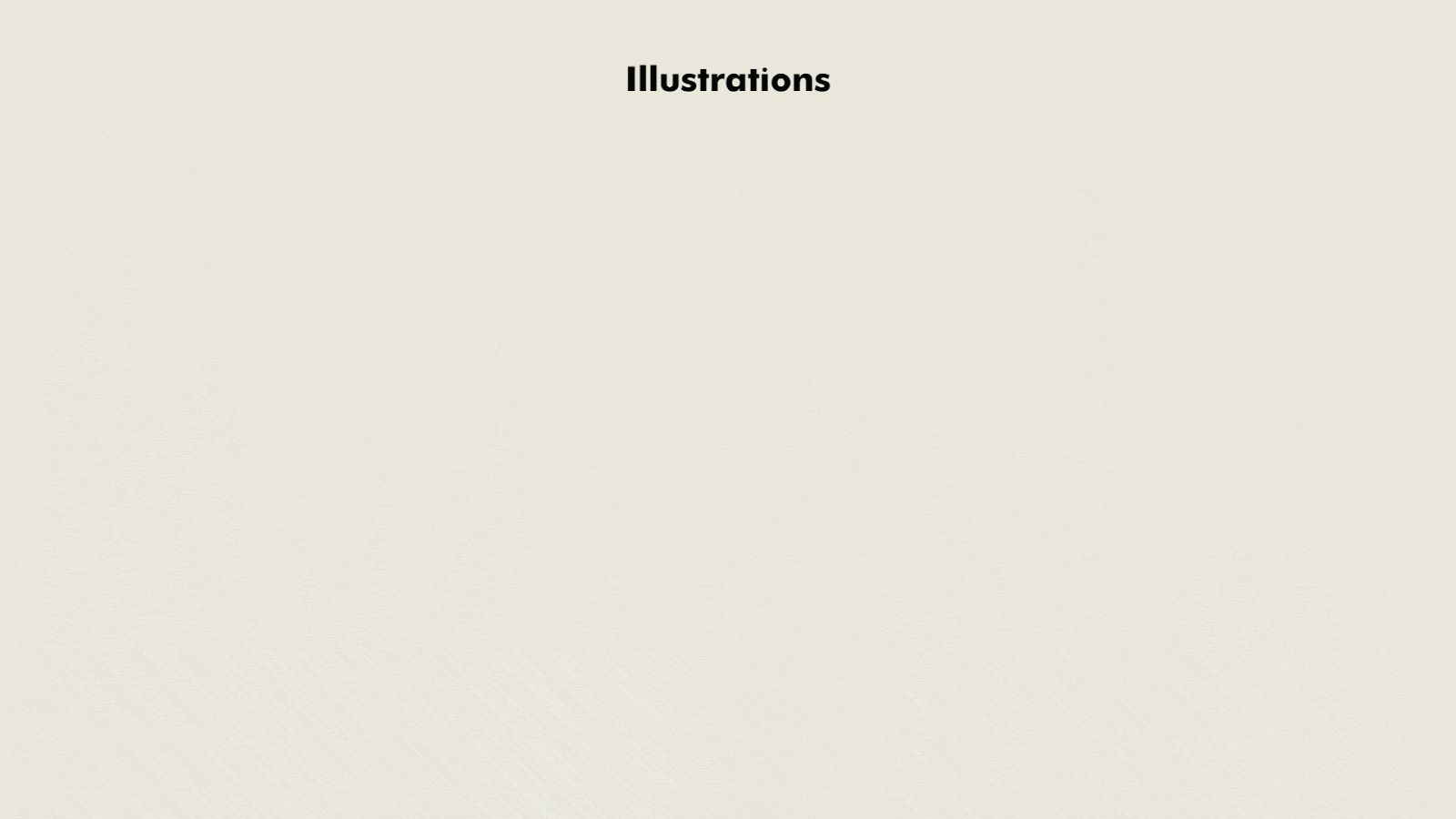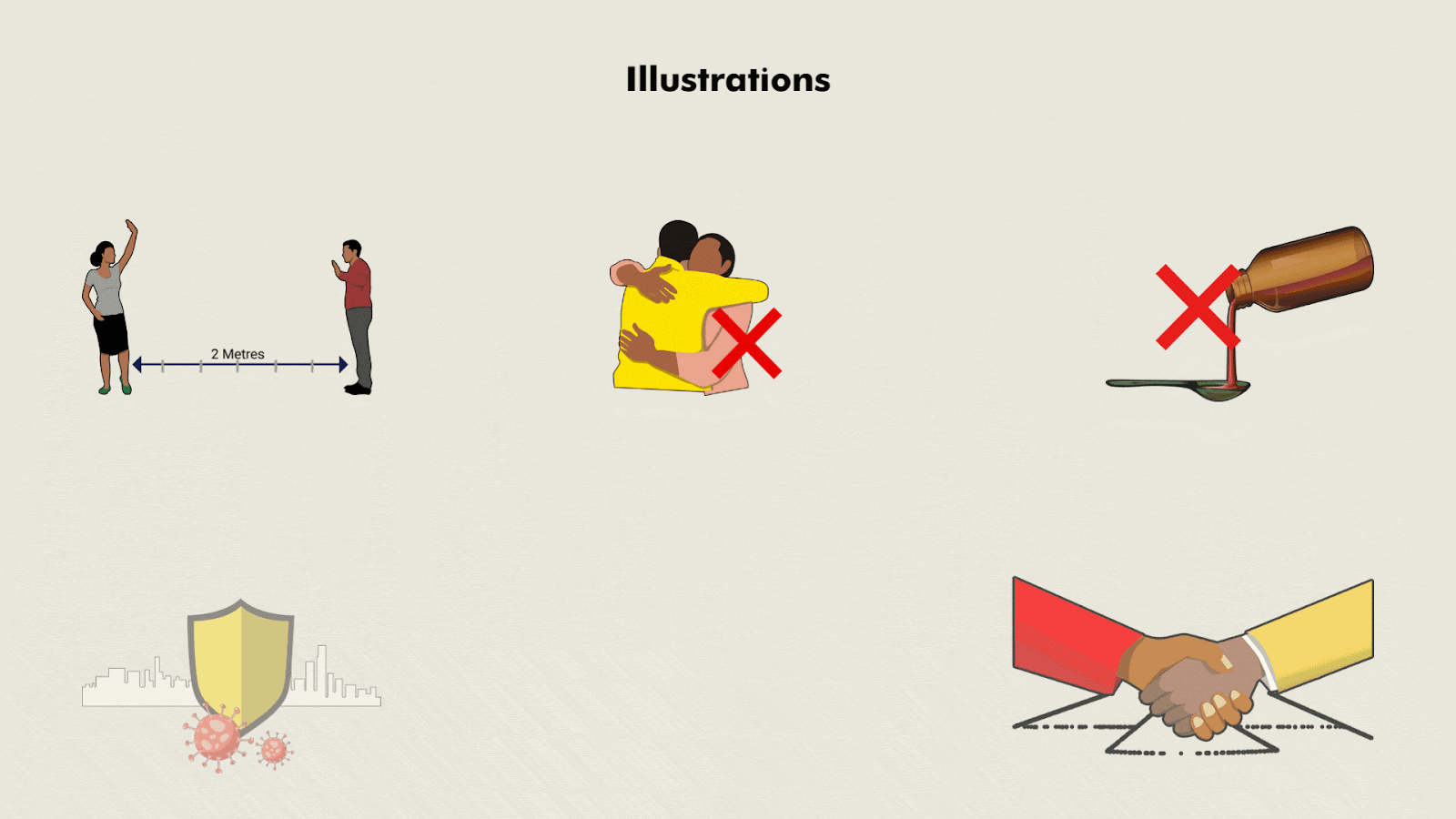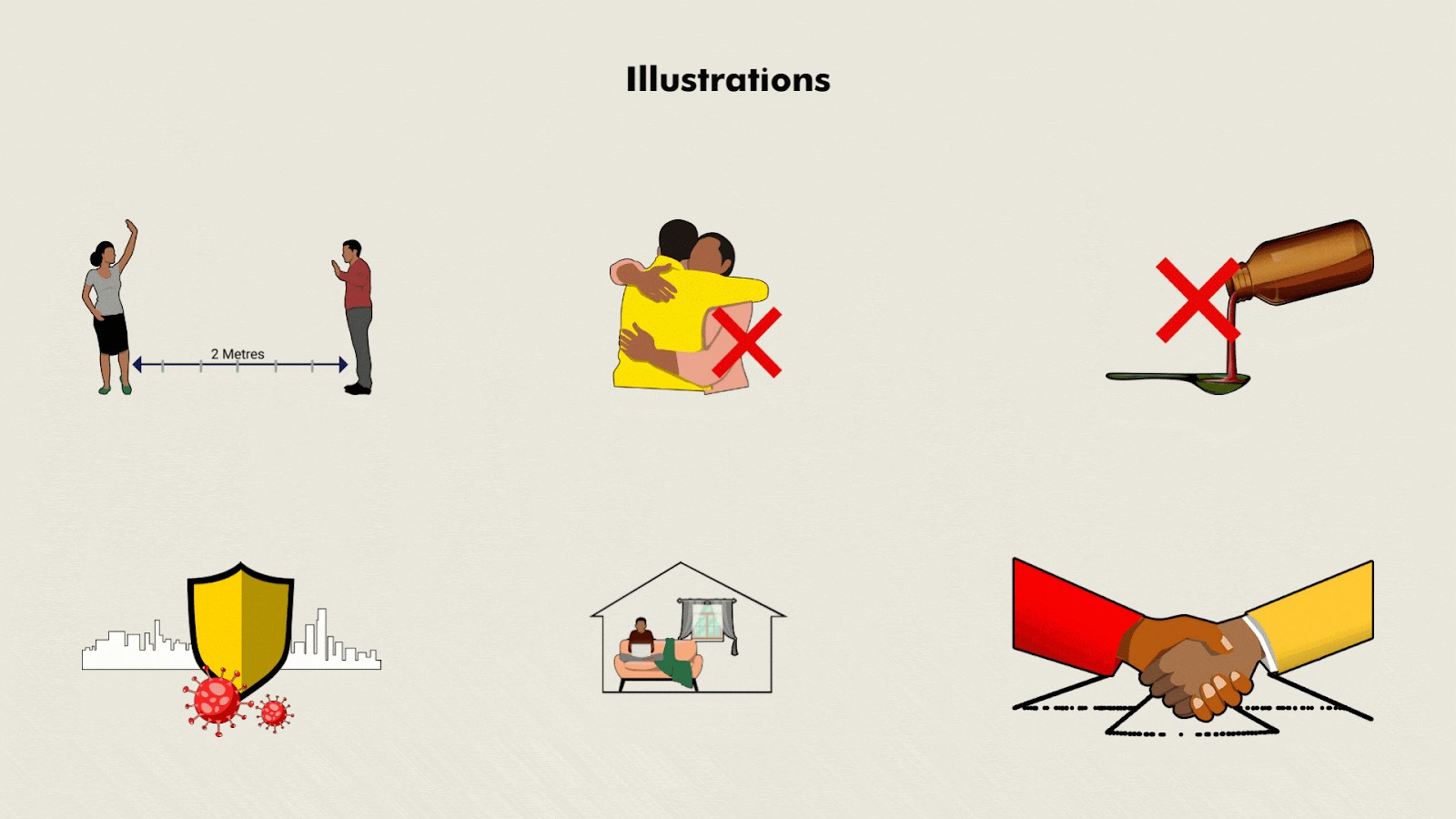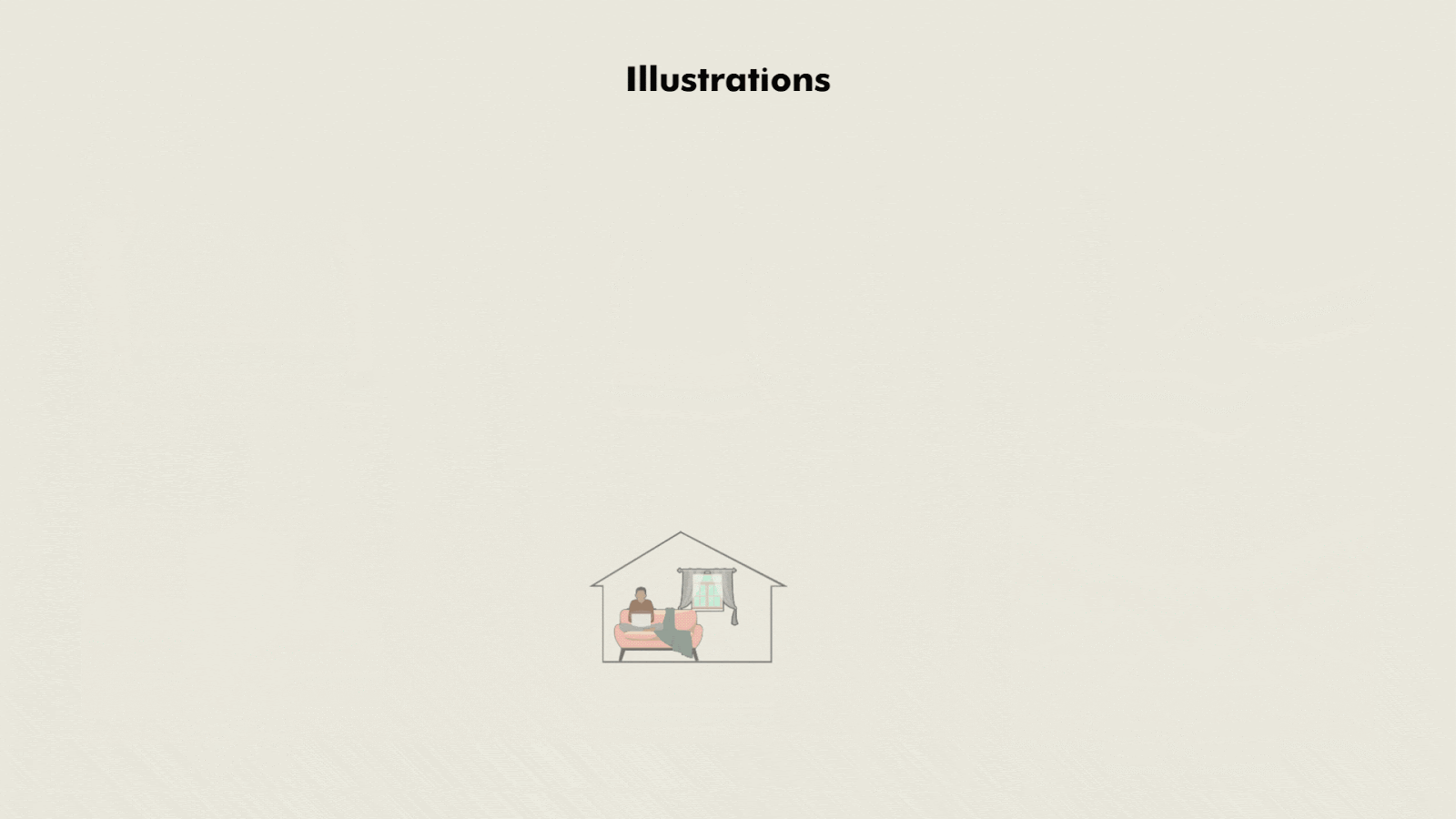
Approach
- Worked with agency leadership and Risk Communications and Community Engagement personnel to understand and document the symptoms, preventive measures, myths, and self-isolation guidance.
- Distilled complex technical information into simpler key messages and call-to-actions in a culturally sensitive and gender-inclusive manner
- Developed visual interpretations including illustrations and artwork towards the development of relevant IEC materials
- Pretested visual interpretations and key messages with key stakeholders and target audience
- Produced IEC materials such as information leaflets/posters, brochures, and audiovisual content for easy dissemination
- Worked closely with the NCDC to develop iterative resources and dissemination strategies in response to the risk communication needs at various stages of the pandemic lockdowns.




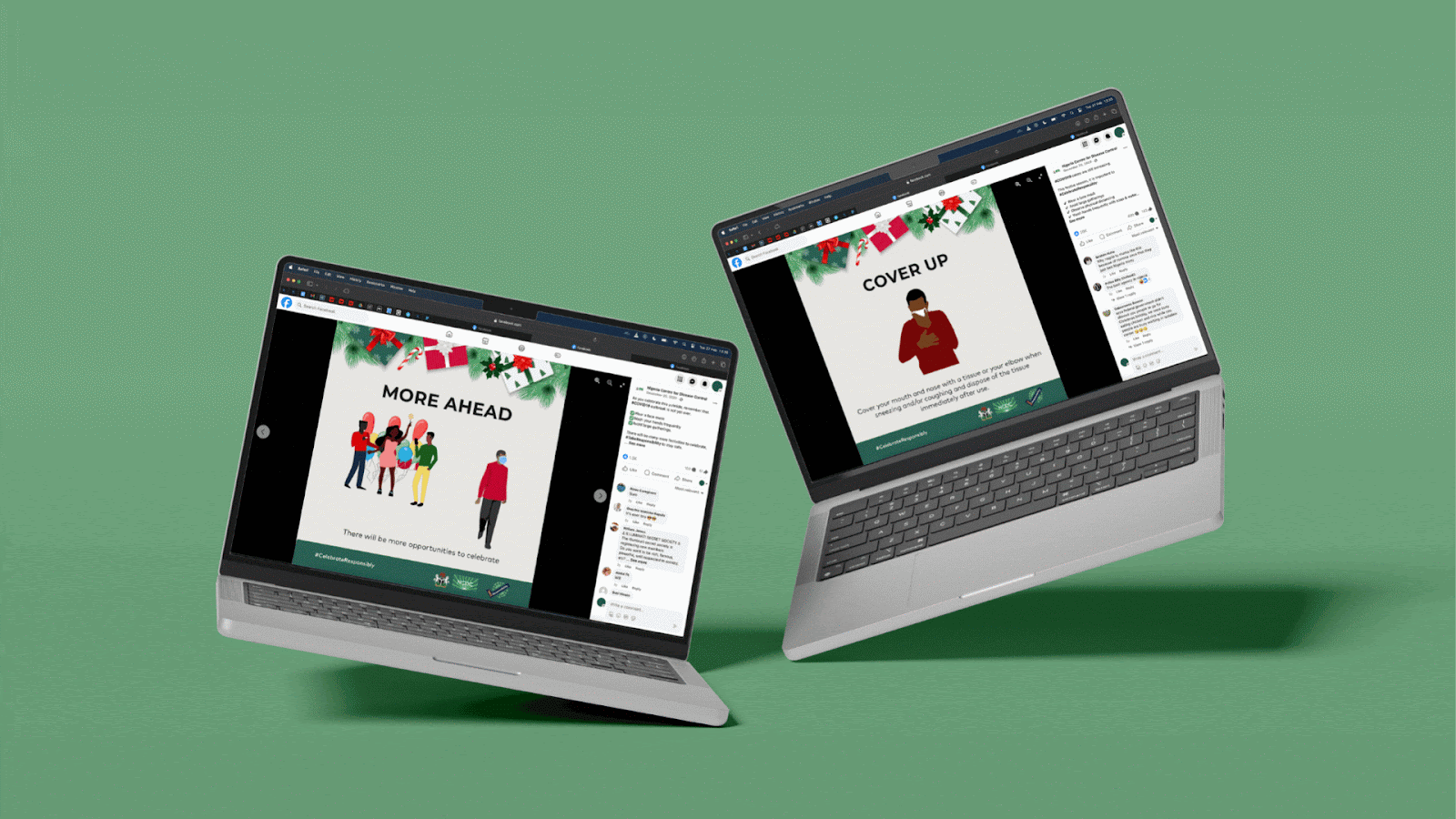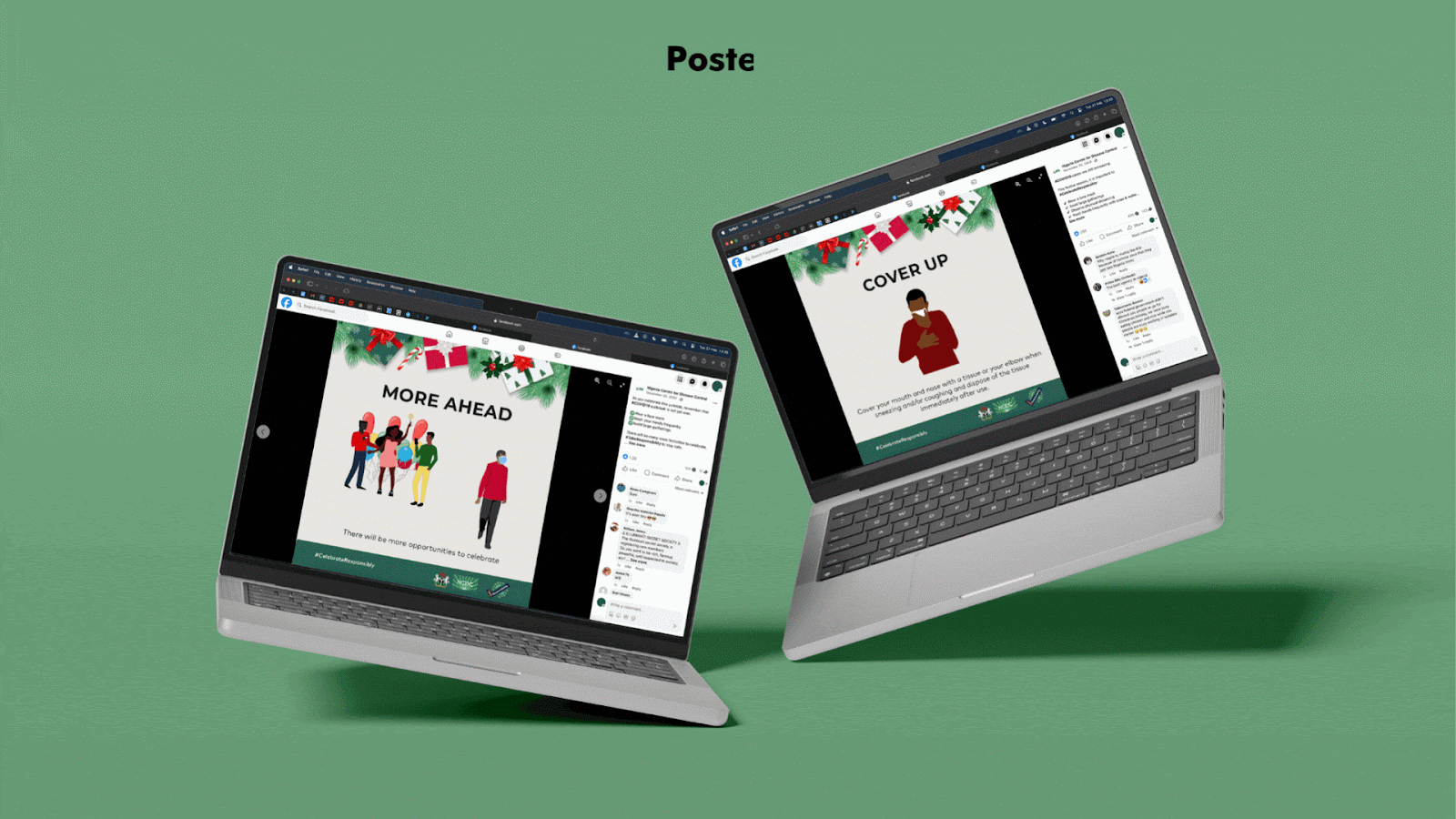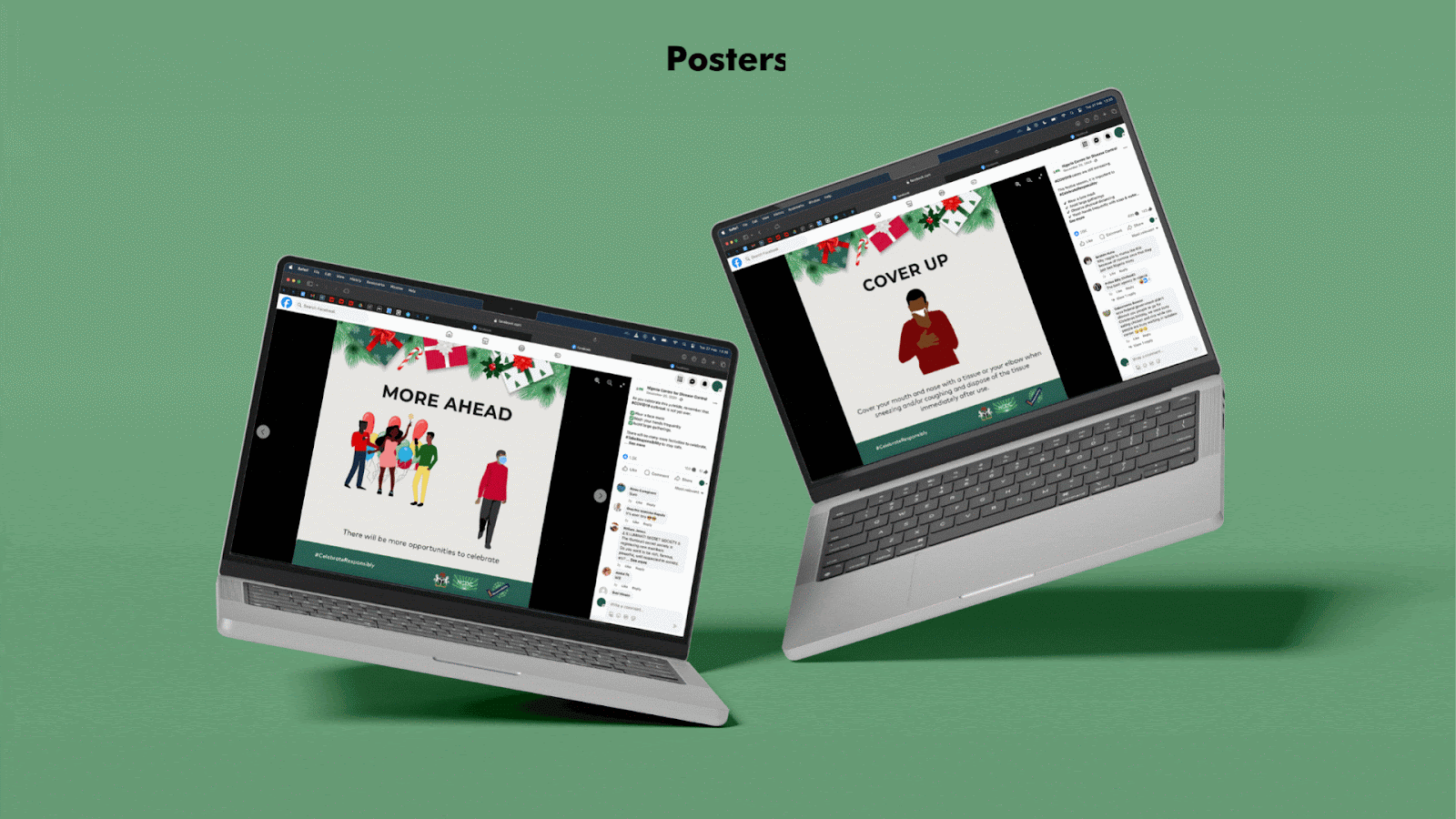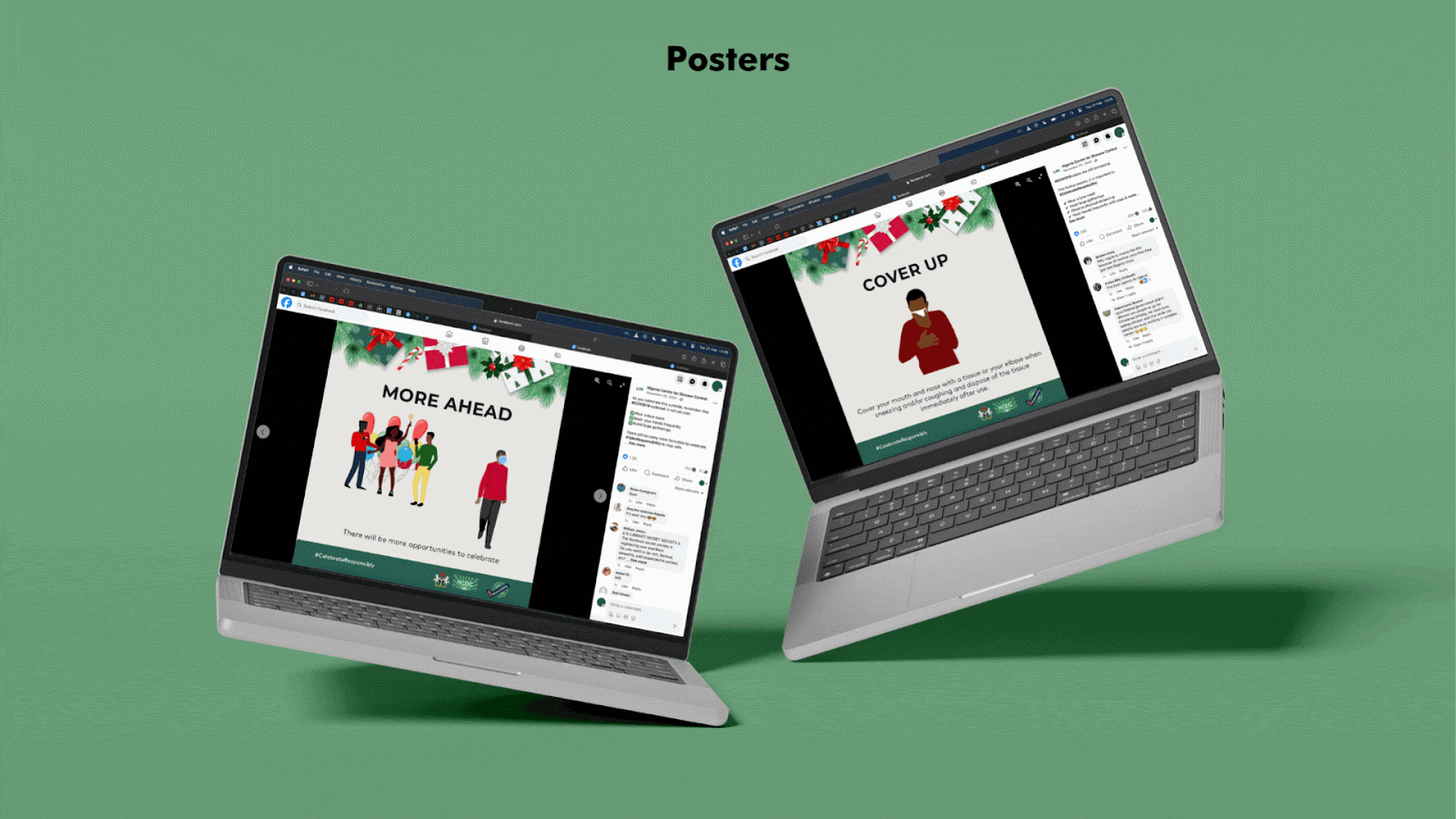
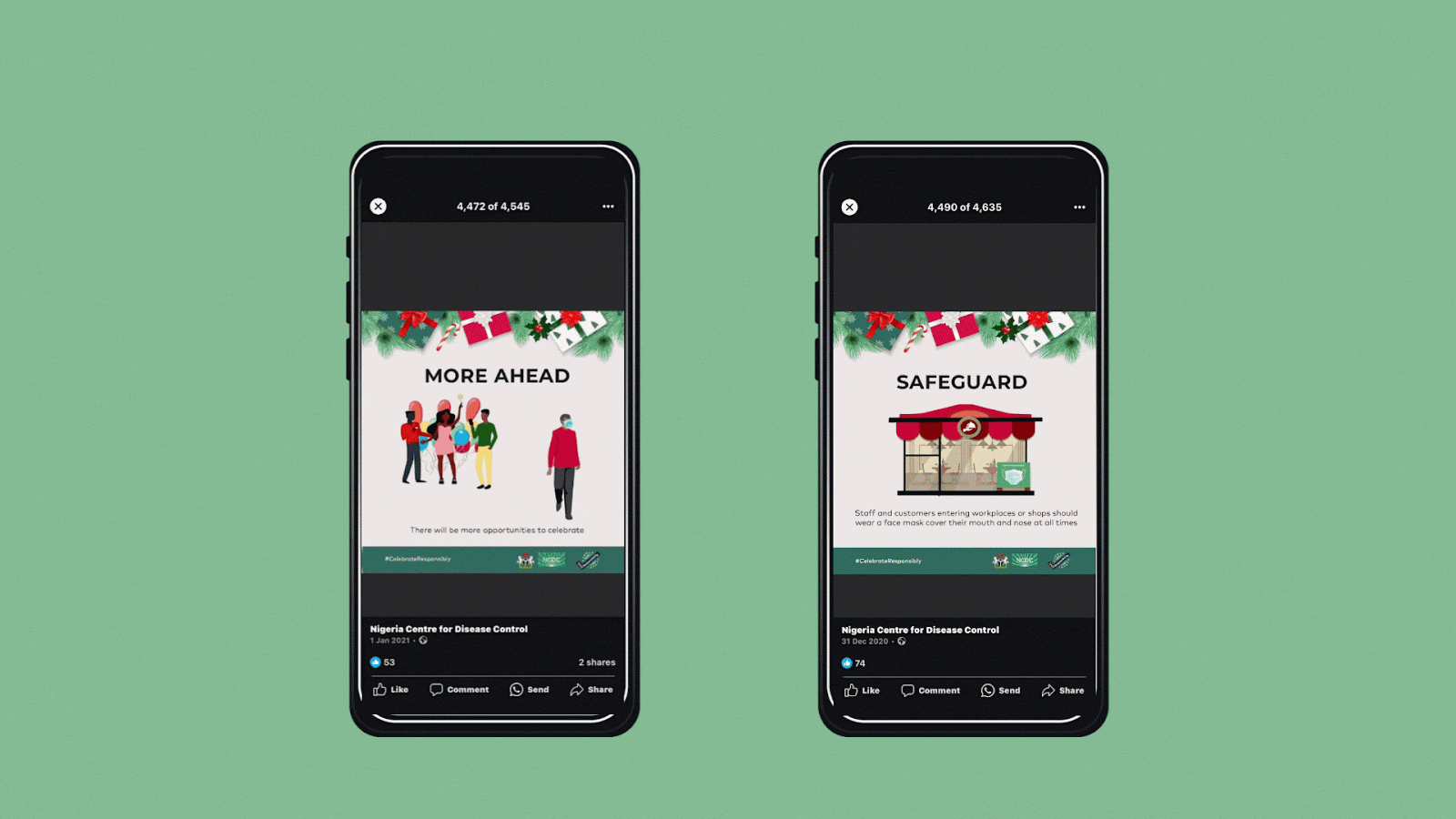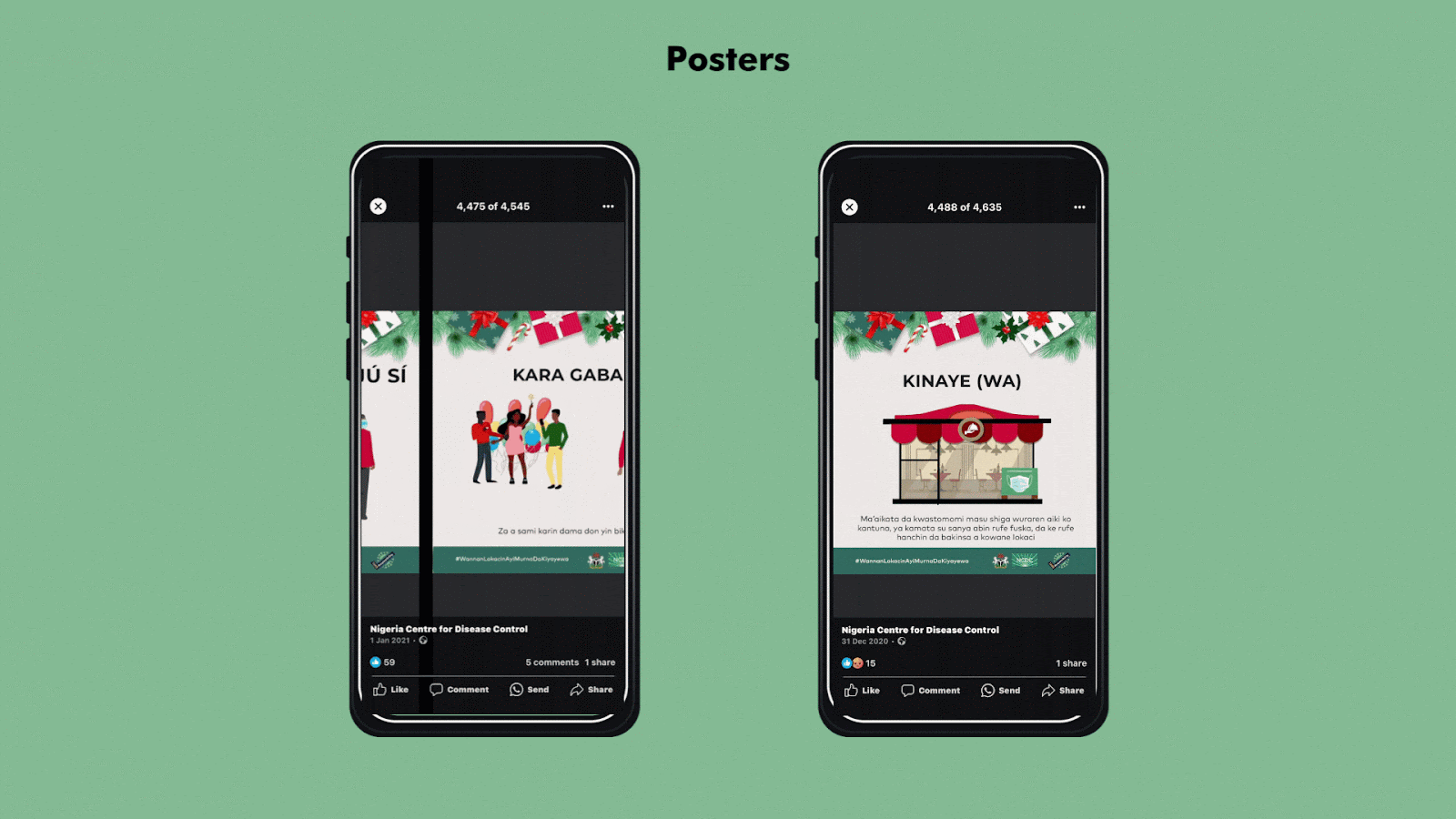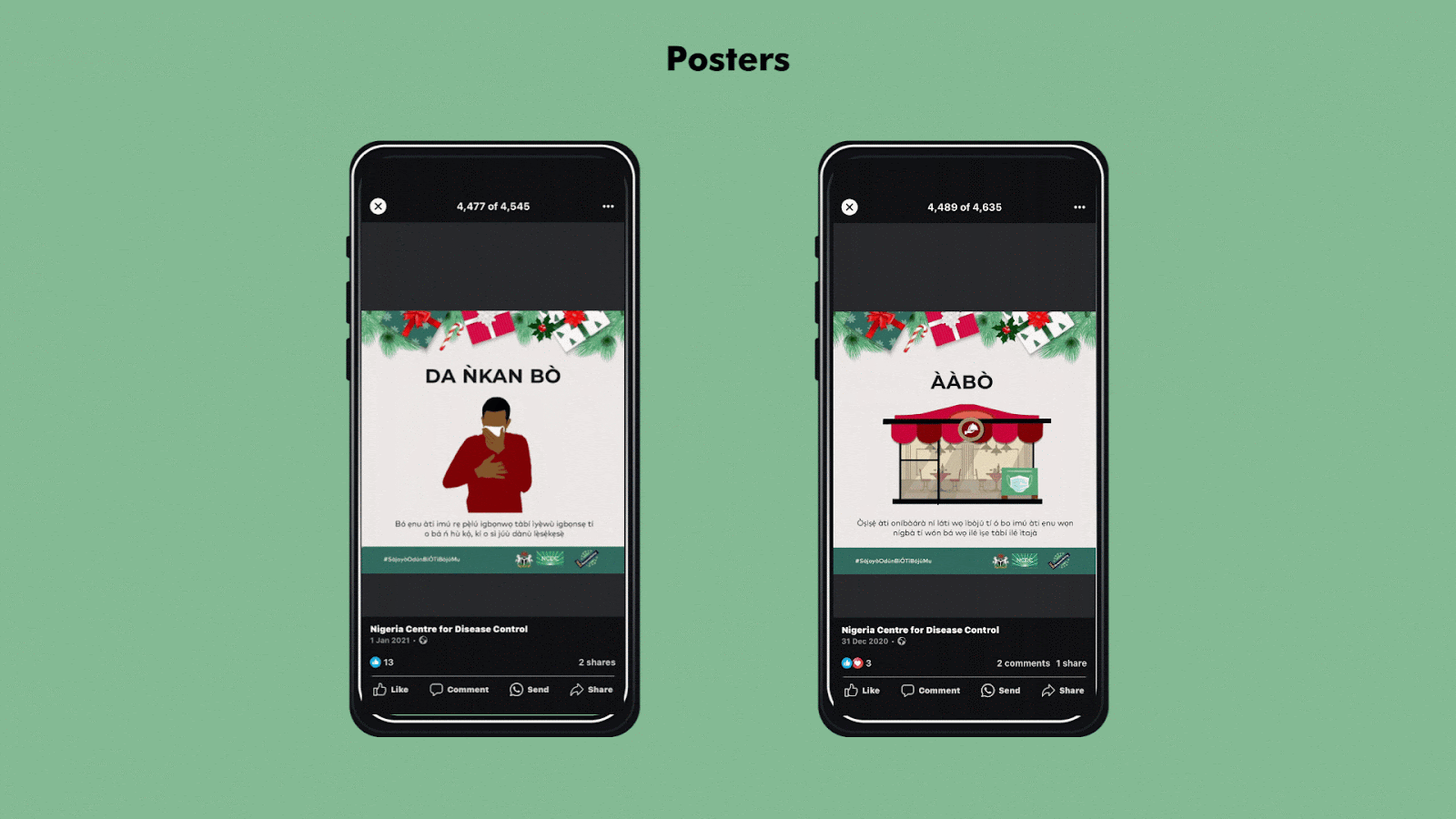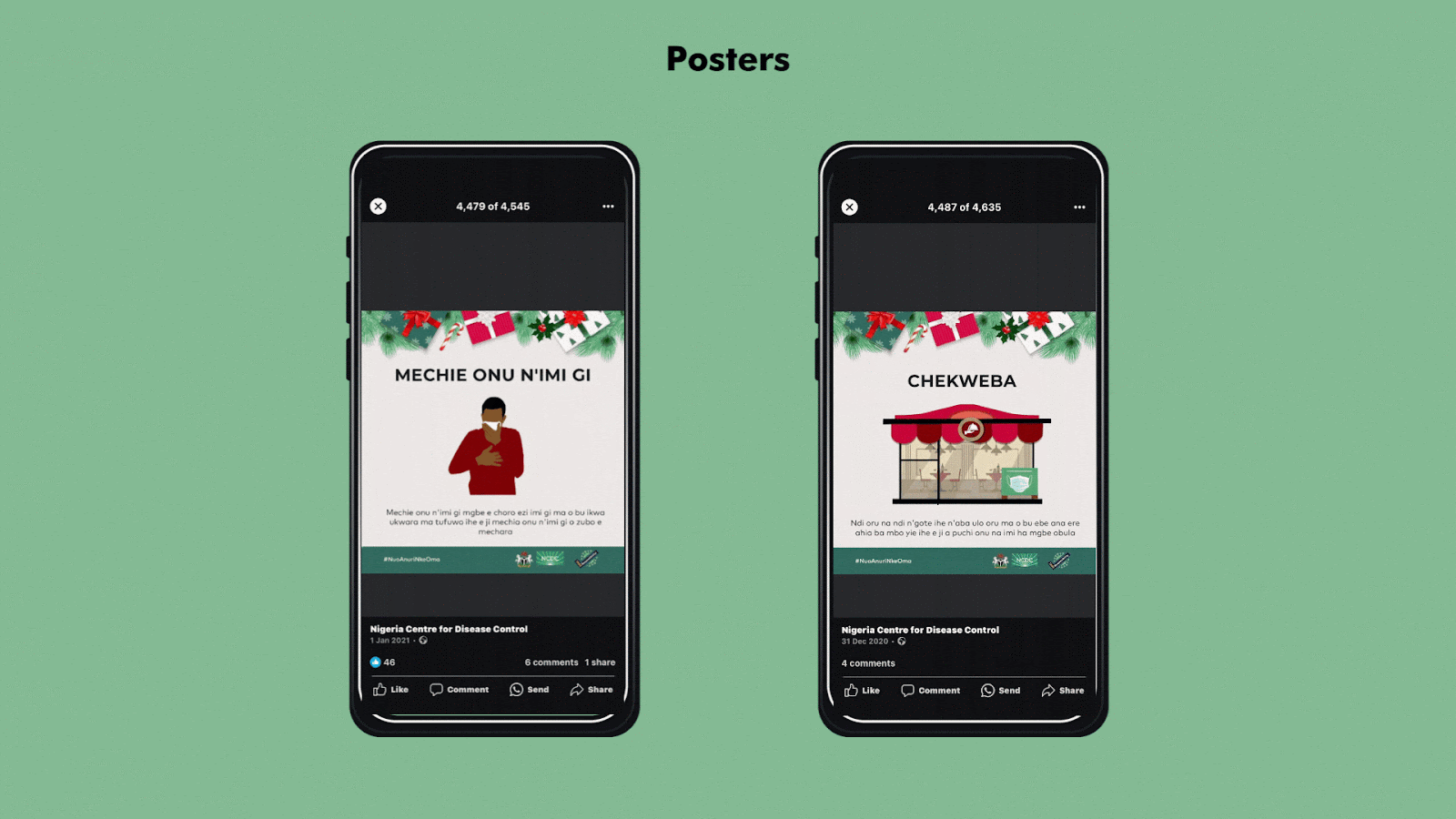
After the easing of the restrictions, messaging focused on safety during the holiday season to prevent the spread of the virus and putting elderly people at risk.
Results
Our COVID-19 risk communications messaging reached and influenced most Nigerians positively. According to a Partnership for Evidence-Based Response (PERC) survey, the majority of respondents believed accurate information about COVID-19 in Nigeria including the efficacy of wearing masks and hand-washing (90% and 91%) to prevent disease transmission. The survey also reported a 78% trust in the NCDC, a significant gain from the baseline.



